Weekend Gardening: Time To Plant Those Fall Vegetables
October 5, 2014
by Santa Rosa Extension
The slightest hint of fall is in the air. But this doesn’t mean that the vegetable gardening season is over. Fall is an excellent time to grow cool-season vegetables.
Florida is unique in that we have multiple growing seasons. There is something that can be grown in the vegetable garden all year round. Knowing which vegetables to grow during which season is the key to having a successful harvest.
In the summer, gardeners are somewhat limited in the different types of warm-season vegetables that can be grown and will survive the heat. Now with cooler days approaching, we have a much wider selection of cool-season vegetables to plant.
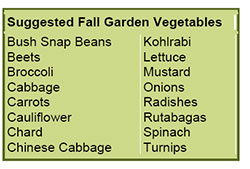
In September many vegetables can be planted in the garden including beets, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, carrots, cauliflower, collards, kale, kohlrabi, leek, lettuce, mustard, onions and radish. In October, you can plant Chinese cabbage, spinach and strawberries.
 These vegetables are best started from transplants but many can be direct-seeded. If you seed them directly into the soil, keep the ground moist while it’s still warm to give them a good start. Keep them well watered if you transplant, too. The later you start, the smarter it becomes to transplant to cut the time to maturity. Preparing the garden properly is as important as selecting the right plants.
These vegetables are best started from transplants but many can be direct-seeded. If you seed them directly into the soil, keep the ground moist while it’s still warm to give them a good start. Keep them well watered if you transplant, too. The later you start, the smarter it becomes to transplant to cut the time to maturity. Preparing the garden properly is as important as selecting the right plants.
Choose a sunny location. Most vegetables perform poorly in shade. An area that receives at least eight hours of sunlight per day is best. Some vegetables such as broccoli, collards and spinach will tolerate partial shade. Avoid locating your garden near hedges or trees. They not only create too much shade but also compete with the garden for moisture and nutrients.
Locating the garden near the house will make it easier to periodically check the garden for insect pests and disease. And, it is easier to keep an eye on the garden for larger pests such as birds, squirrels and rabbits. Closeness to the house will make it convenient in tending to the garden chores.
 Locate the garden near a water supply so it can be watered as needed. You’ll get only moderate results if you try to grow a garden without supplemental irrigation.
Locate the garden near a water supply so it can be watered as needed. You’ll get only moderate results if you try to grow a garden without supplemental irrigation.
Of course, it’s important to prepare beds properly before planting. To do that, clear the site of all weeds or finished vegetable plants. Turn the soil with a shovel, fork or tiller to a depth of at least 8 inches, and spread a 2-inch to 4-inch layer of organic matter (leaves, grass clippings, aged manure or compost) over the tilled soil. This helps to maintain a high level of organic matter in the soil, which encourages a strong, healthy root system, improves drainage, retains moisture, provides nutrients and promotes vigorous plant growth.
Mix the organic matter thoroughly into the soil. Turn the soil by digging with a shovel, garden fork or a tiller until the materials you’ve added are evenly distributed in the soil. When using fresh organic amendments, it’s best to wait a couple of weeks before planting your transplants or seeds.
By this time of year, insects and diseases have had all summer to build up their populations. Insects such as whiteflies, stink bugs, aphids and caterpillars are commonly seen. Since insect and disease pressure often is greater in the late summer/early fall than in the spring, watch plants carefully for problems and use appropriate control measures promptly when needed. Contact your local Extension Office for control recommendations.



Comments